CyberSec and Quantum Computing
1. Introduction
In this guide, we’ll delve into the fascinating world of quantum computing, exploring its potential impact on our lives and the critical security concerns it raises. This article was written using ChatGPT since I’m not an expert in quantum computing or cybersecurity, but I found this content interesting, that’s why I decided to put some effort on adjusting this so that It sounded more like something I would say and share it.
Quantum computing is an emerging field that harnesses the principles of quantum mechanics to perform calculations at speeds that are just unimaginable with classical computers. This guide aims to demystify quantum computing and explore how it will shape our future, particularly in the realm of cybersecurity. However before talking about quantum computing, we need to talk about quantum physics, since there’s a strong relation in those two worlds.
2. Understanding Quantum Physics
Quantum physics, also known as quantum mechanics, is a branch of physics that deals with the behavior of particles at the quantum level, where classical physics fails to provide a complete description. It introduces us to a world that is both fascinating and counterintuitive, governed by a unique set of principles:
2.1 Superposition
Superposition is a fundamental concept in quantum physics. It states that particles, such as electrons or photons, can exist in multiple states simultaneously. In the quantum realm, a particle can be in a superposition of multiple positions, energies, or other properties.

2.2 Entanglement
Entanglement is another intriguing phenomenon. When two particles become entangled, their properties become correlated in such a way that the state of one particle instantly influences the state of the other, even if they are separated by vast distances.
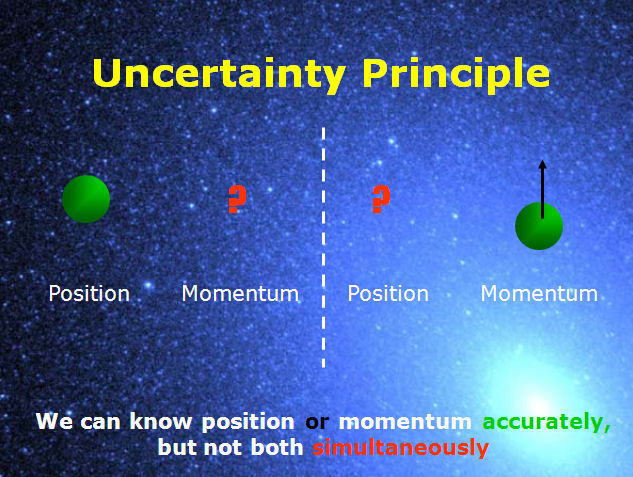
2.3 Uncertainty Principle
The uncertainty principle, famously formulated by Werner Heisenberg, states that certain pairs of physical properties, like a particle’s position and momentum, cannot be precisely measured simultaneously. The more accurately you know one property, the less you can know about the other.
3. What is Quantum Computing?
Now, let’s bridge the connection between quantum physics and quantum computing:
3.1 Quantum Bits (Qubits)
Quantum computing relies on the principles of quantum physics to process information. Instead of classical bits (0s and 1s), quantum computers use qubits. Qubits can exist in a superposition of states, meaning they can represent both 0 and 1 simultaneously. This property allows quantum computers to perform certain calculations exponentially faster than classical computers.

3.2 Quantum Gates
Quantum gates are the building blocks of quantum circuits, akin to classical logic gates. However, they manipulate qubits in ways that exploit quantum phenomena such as superposition and entanglement to perform complex computations.
3.3 Quantum Algorithms
Quantum algorithms, like Shor’s algorithm and Grover’s algorithm, harness the unique properties of qubits to solve problems that would be practically impossible for classical computers. For instance, Shor’s algorithm can efficiently factor large numbers, posing a significant threat to classical encryption methods.

4. Quantum Computing’s Quantum Foundation
Quantum physics and quantum computing share a deep-rooted relationship. Quantum computing harnesses the strange yet powerful principles of quantum mechanics to unlock computational capabilities that were once the stuff of science fiction. As we continue to advance in both fields, we can anticipate a future where quantum computing plays a pivotal role in solving complex problems, revolutionizing industries, and reshaping our understanding of computation itself.
In this quantum journey, we’ve explored the quantum world’s connection to quantum computing, highlighting how the principles of quantum physics drive the innovation and potential of this groundbreaking technology. Keep exploring the quantum realm and its applications, for there’s much more to uncover in this entangled and superposed universe of possibilities.
5. Quantum Computing’s Role in Everyday Life
Quantum computing promises to revolutionize several industries, including:
5.1 Advancements in Drug Discovery
Quantum computers can simulate complex molecular structures, accelerating drug discovery and the development of new medications.

Why did the quantum computer went to the pharmacy?
To get some “byte”-amins for its quantum health!
5.2 Optimizing Supply Chains
By solving complex optimization problems in real-time, quantum computers can streamline supply chains, reducing costs and environmental impact.
5.3 Cryptography and Data Security
Quantum computing also poses significant challenges to data security, as it can break widely used encryption methods. Let’s explore this in detail.
6. Security Concerns with Quantum Computing
6.1 Shor’s Algorithm and RSA Encryption
Shor’s Algorithm, when executed on a quantum computer, can efficiently factor large numbers. This threatens the security of RSA encryption, widely used for secure communication.
6.2 Post-Quantum Cryptography
To counter quantum threats, researchers are developing post-quantum cryptographic methods, which are believed to be secure against quantum attacks.
6.3 Quantum Key Distribution (QKD)
QKD leverages the principles of quantum mechanics to provide secure communication channels, immune to quantum attacks.
7. Conclusion
Quantum computing is on the cusp of transforming various aspects of our lives, from healthcare to logistics. However, it also presents formidable challenges in the realm of cybersecurity. Staying informed about these developments is crucial as we navigate this quantum-powered future.
8. Further Resources
For a deeper dive into quantum computing and cybersecurity, consider exploring these resources:
- What is quantum computing?
- NIST Post-Quantum Cryptography Standardization
- Quantum Computing and Cryptography Research Papers
Thank you for joining us on this quantum journey. Embrace the future and stay secure!
